

This will lead the script into a recursive loop which you can only get out of by closing your terminal window.īecause the mysql_secure_installation script performs a number of other actions that are useful for keeping your MySQL installation secure, it’s still recommended that you run it before you begin using MySQL to manage your data. Please consider using ALTER USER instead if you want to change authentication parameters. Failed! Error: SET PASSWORD has no significance for user as the authentication method used doesn't store authentication data in the MySQL server. This script changes some of the less secure default options for things like disallowing remote root logins and removing sample users. Step 2 - Configuring MySQLįor fresh installations of MySQL, you’ll want to run the database management system’s included security script. Because this leaves your installation of MySQL insecure, we will address this next.
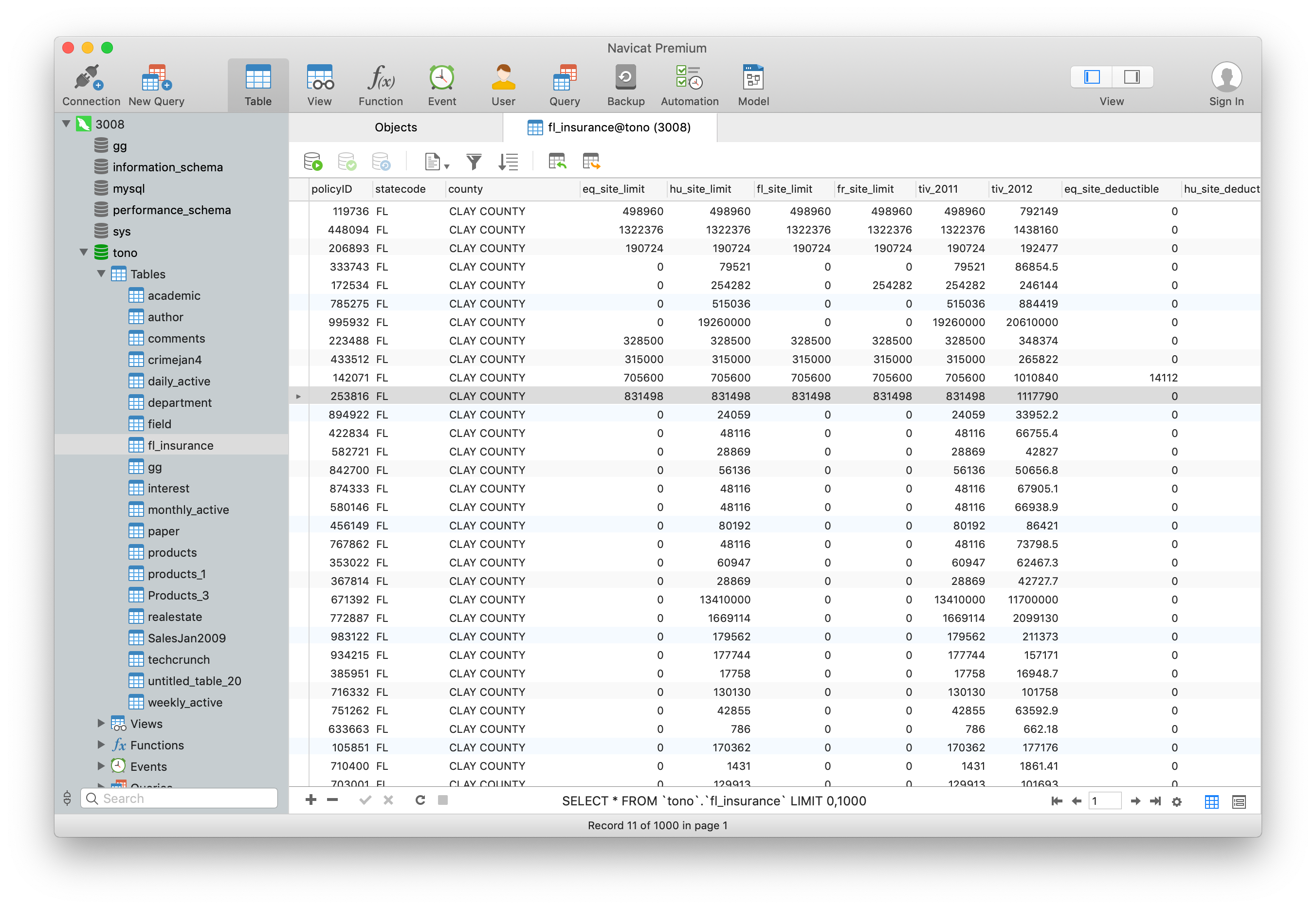
These commands will install and start MySQL, but will not prompt you to set a password or make any other configuration changes. To install it, update the package index on your server if you’ve not done so recently:Įnsure that the server is running using the systemctl start command: At the time of this writing, the version of MySQL available in the default Ubuntu repository is version 8.0.28. On Ubuntu 22.04, you can install MySQL using the APT package repository. To set this up, follow our initial server setup guide for Ubuntu 22.04.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
